What is Google Antigravity: The Future of Agent-Driven Software Development
Introduction
In late 2025, Google introduced Antigravity as a radical new platform for software development. It shifts the paradigm from “AI assisting a human” to “AI agents collaborating as developers.” In this article we’ll cover:
-
What Antigravity is and how you use it
-
Its key features, strengths and weaknesses
-
How it stacks up against Cursor and n8n
-
What these differences mean in practice
-
Where this space might go next
What Is Google Antigravity & How It Works
Overview
-
Antigravity is an “agent-first” development platform by Google, built on its new model Gemini 3 Pro. blog.google+2Venturebeat+2
-
Public preview launched November 18, 2025 for Windows, macOS and Linux. Vikipedi+1
-
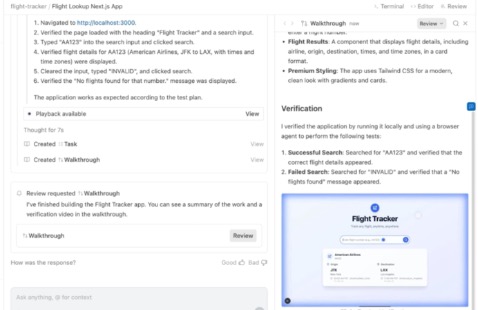
Key idea: rather than just offering suggestions, Antigravity gives AI agents direct access to tools — code editor, terminal/shell, browser — so they can plan, execute and report outcomes. Venturebeat+1
How It Works: User Flow
-
Agent creation: You define a high-level task or goal (for example: “Build a dashboard with live data and tests”).
-
Agent access: The agent uses the code editor environment, runs commands in the terminal, opens a browser, executes tests.
-
Artifacts & verification: The agent generates “Artifacts” such as task lists, screenshots, browser recordings, summaries of what it did and plans next. The Verge+1
-
Two main views:
Key Features at a Glance
-
Multi-agent orchestration: spawn and monitor multiple agents working concurrently.
-
Full tool-access: agents aren’t limited to code suggestions—they can execute and deploy.
-
Artifact-based traceability: what the agent did and plans to do is visible & auditable.
-
Model flexibility: while Gemini 3 Pro is the core, platform reportedly supports other models too. The Verge
-
Free preview: currently available at no cost (but with rate-limits) during the preview phase. The Times of India
Strengths of Antigravity
-
High autonomy: Agents can take on entire development tasks rather than just filling in code lines.
-
Full integration: Editor + terminal + browser in one platform means fewer tool-switches.
-
Team & scale oriented: With multi-agent and Manager View, it’s built for more than solo coding.
-
Transparency built-in: Artifact system provides insight into what agents did, which increases trust.
-
Backing & ecosystem: Built by Google, leveraging cutting-edge model Gemini 3 Pro.
Weaknesses & Considerations
-
Early stage / Preview: As a new platform, there may be bugs, missing features, and instability.
-
Learning curve: Developers must adapt to thinking in “tasks + agents” rather than just “write code”.
-
Ecosystem lock-in risk: Deep integration with Google stack means migrating away later might be harder.
-
Overkill for simple tasks: If you just need simple autocomplete or code suggestion, this platform may be heavier than needed.
-
Security & oversight: Granting agent access to terminal/browser raises new risks (shell commands, browser automation) — oversight is required.
Pricing & Licensing
-
Currently: Free in public preview with “generous rate limits” on usage. The Verge+1
-
Full pricing for post-preview or enterprise usage not yet fully published.
-
Given model usage (Gemini 3 Pro) and deep features, future cost is likely to be significant for large teams.
Comparing Antigravity to Cursor & n8n
Overview of Competitors
Cursor (by Anysphere)
-
AI-powered code editor (fork of VS Code) focused on developer productivity, deep code-base understanding, and refactoring. DataCamp+1
-
Features include smart rewrites, indexing entire codebase, prompt-based refactoring. Medium+1
-
Pricing & mode: Token-based pricing, request-based usage (as of mid-2025). Cursor+1
n8n
-
Workflow automation platform (node-based visual builder) for integrating apps, automating business processes, dev-ops flows. n8n.io
-
Plans start at ~€20/month for 2.5k executions in cloud. n8n.io+1
-
Focus is not “write code editor”, but “connect & automate systems and workflows”.
Feature Comparison Table
| Platform | Primary Focus | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antigravity | Agent-first development (editor + orchestration) | Multi-agent, full tool access, high automation | New, possibly complex for simple dev tasks |
| Cursor | AI-enhanced code editor for developers | Deep code-base understanding, refactoring support | Limited orchestration, not full agent platform |
| n8n | Workflow & automation across tools/services | Visual automation, many integrations | Not built for code editing or full agent dev workflows |
How They Differ in Practice
-
Task Scope:
-
Antigravity: Build entire features via AI agents (code, test, deploy).
-
Cursor: Enhance your coding workflow (autocomplete, refactor, fix bugs).
-
n8n: Automate processes (data pipelines, API integrations, business logic).
-
-
Workflow Complexity:
-
Antigravity: High — multi-agent, full dev stack.
-
Cursor: Medium — daily coding tasks, refactoring, productivity.
-
n8n: Variable — depends on number of integrations and workflows.
-
-
Tool Switching:
-
Antigravity aims to reduce switching (editor + terminal + browser in one).
-
Cursor still primarily editor-centric, may use other tools for terminal/browser.
-
n8n focuses on workflows, less on code writing environment.
-
-
Team vs Solo Developer Fit:
-
Antigravity: Best for teams working on large codebases or multiple agents.
-
Cursor: Very good for individual devs or smaller teams focusing on code.
-
n8n: Ideal for teams automating integrations, ops, less writing new features.
-
Use-Case Example
-
Suppose you need to build a microservice including API, UI, tests, deployment:
-
Use Antigravity: spawn an agent “Build microservice”, let it scaffold backend, UI, test, deploy, then review.
-
Use Cursor: You write code; Cursor helps you refactor quickly, understand your codebase, generate tests.
-
Use n8n: You automate the pipeline: webhook triggers build → test → deploy → notify Slack.
-
Why This Matters & Future Outlook
Why It Matters
-
The shift from “AI suggestion” to “AI agent” reflects the next phase of developer tooling. Antigravity is a major step in that direction.
-
As codebases grow and teams expand, higher-level abstraction becomes more necessary: you want to manage tasks, not type every line.
-
Having fewer context-switches (editor + terminal + browser) improves efficiency and reduces cognitive load.
-
Integrations and automation (n8n-style) are becoming part of developer workflows, not just business-ops workflows.
Future Trends & What to Watch
-
Agent ecosystems: More platforms will provide agent orchestration, specialized agents, plug-and-play agents for dev tasks.
-
Model improvement: Models like Gemini 3 Pro show that tool-use (terminal/browser) is now viable; this will improve further. blog.google
-
Security & governance: With agents having elevated access (shell, browser), governance, traceability, artifact logs will become critical.
-
Hybrid workflows: Platforms may combine elements: editor + automation + orchestration + business workflows.
-
Accessibility & pricing: As these platforms become mature, pricing, usage-models, and democratization will matter (not just for big companies).
Final Thoughts
Google Antigravity is a bold vision of what developer tools could become: where you delegate entire tasks to AI, monitor them, and focus on high-level design. It’s powerful, built on top of Gemini 3 Pro, and supports a future where agents do more of the heavy lifting.
That said, if you’re an individual developer today working on code, you may still prefer a tool like Cursor for daily workflow enhancements. If you’re more about automating workflows and systems rather than writing fresh code, then n8n remains a strong choice.
In short:
-
For full agent-driven development → Antigravity
-
For refined code editing + AI assistance → Cursor
-
For workflow automation and integrations → n8n
If you like, I can draft a downloadable PDF of this article (formatted for blog posting) or prepare screenshots & demo workflows showing Antigravity vs Cursor vs n8n side-by-side.